By Deni Hui, The University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy
Curist delivers over-the-counter medicines to your door at a fraction of the price of traditional brands. We hope everyone stays safe and healthy during this time.
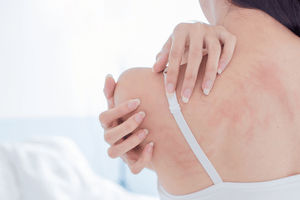
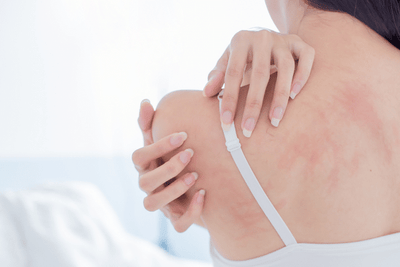
Have you ever broken out in hives and felt the itchy red bumps on your skin? For most people, hives are usually more than just a temporary nuisance. Read along to learn more about what hives are and what you need to know about them!
What are Hives (Urticaria)? How Long Do Allergic Hives Last?
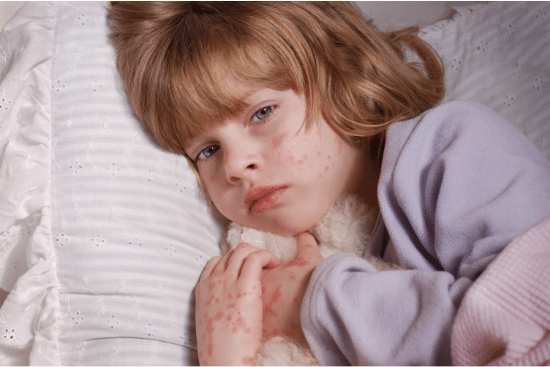
Hives (also known as urticaria) are a common skin reaction to an allergen (a substance that causes allergies). About 20% of people will develop hives at least once in their lifetime. Though uncomfortable, It is a harmless skin condition marked by spots on the skin that are itchy, red, and raised. Hives are usually a temporary condition, and there are two different types of hives, acute hives (acute urticaria) and chronic hives (chronic urticaria).
- Acute Hives (Urticaria): Short term, most likely allergy-related rash that fades in 2-3 hours but could hold on for as long as six weeks.
- Chronic Hives (Urticaria): Long term, auto-immune related rash that lasts longer than six weeks.
What Causes Hives?
Hives are the classic sign of an allergic reaction, although hives can erupt for other reasons including:
- Allergens (contact urticaria) like pollen, ragweed, mold spores or pet dander
- Insect stings or bites
- Poisonous plants (e.g. poison ivy, poison oak)
- Foods (e.g. milk, peanuts, eggs, fish or shellfish)
- Chemicals
- Medications (e.g. NSAIDs like ibuprofen, aspirin; codeine, blood pressure medicine)
- Infections (e.g. Strep throat or urinary tract infections)
- Emotional stress
- Autoimmune disorders
- Physical causes (physical urticaria) such as cold (cold urticaria), sweating (cholinergic urticaria), water, or sun exposure.
What are the Symptoms of Hives?
Hives can appear anywhere on your body and can vary in appearance depending on the person and the situation, but the main sign of hives is the hallmark red raised welts. The welts from hives can:
- have a pale center (turns white when pressed)
- appear in clusters
- change shape and location in a matter of hours
- be tiny or as big as a dinner plate
- itch, sting, or cause a burning sensation
- swelling (or angioedema) around eyes, lips, feet or throat
It is important to note that rarely, a person with hives and angioedema can also get anaphylactic shock which include signs of trouble breathing, a drop in blood pressure, or a loss of consciousness. If this situation ever occurs, make sure to seek medical attention immediately.
What is the Difference Between Acute vs Chronic Hives (Urticaria)?
The main differences between acute and chronic hives (urticaria) are how long the symptoms last and what their respective triggers are. Acute hives are short-term; they can last for less than a day or up to six weeks. They can be triggered by coming into contact with an allergen such as food, animal dander, insect bite, latex or pollen. Acute hives can also occur from non-allergic causes such as heat, exercise or stress. Being able to identify and avoid these triggers can help prevent this allergic reaction from occurring.
Chronic hives, on the other hand, can stick around for a longer period of time (more than 6 weeks). Most chronic hives are idiopathic, meaning that the exact cause is unknown. Only a small percentage of chronic hives are due to an allergic reaction.
Regardless of whether you have acute or chronic hives (acute or chronic urticaria), antihistamines will be your mainstay of treatment options to help relieve symptoms.
What is the Difference Between Hives vs Skin Rash?
Hives (urticaria) are a particular type of skin rash. They are raised, itchy red bumps that can be large or small in size. Skin rash, on the other hand, can take many other forms often characterized by changes in color or texture of the skin. They can cause your skin to feel rough and look scaly or cracked. Unlike hives, rashes don’t always itch. Sometimes, they hurt or make your skin feel irritated, scratchy or uncomfortable.
How Long Does it Take for Hives to Go Away? How Do You Get Rid of Hives Fast?
Hives are often a temporary skin reaction that can go away in 2 to 3 hours without treatment. However, in some people, hives can persist for weeks or months.
Even though hives typically resolve in a couple of hours, over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines are recommended as treatment options because they provide the quickest route to symptom relief. Anti-itch lotions, creams as well as topical anesthetics can provide instant relief from the pain and itchiness of hives, but they will not relieve the swelling or redness. Thus, antihistamines are best recommended for quick overall symptom relief.
Do Antihistamines Treat Hives? Do Antihistamines Make Hives Go Away?
For acute cases of hives (acute urticaria), some of the best antihistamines are well-known over-the-counter antihistamines such as Curist Allergy Relief (levocetirizine), (fexofenadine (brand Allegra), diphenhydramine (brand Benadryl), loratadine (brand Claritin), and cetirizine (brand Zyrtec) can help reduce swelling, redness, itching, and other problems such as wheezing or difficulty breathing. Chronic hives (chronic urticaria) are usually treated with a three to six month regimen of antihistamines. For chronic hives, it’s recommended to use a newer antihistamine like levocetirizine which does not have the same sedating side effects like Benadryl.
If none of the antihistamines work, consult your doctor or pharmacist as they may also add a different type of antihistamine called an histamine-2-receptor blocker, such as ranitidine or cimetidine. These medications are usually used to treat acid reflux but can also help with reducing hives.
Is There a Non Drowsy Antihistamine for Hives?
Yes, there are non drowsy antihistamines for treating hives, for instance Curist Allergy Relief (levocetirizine) which is minimally drowsy! Fexofenadine (brand Allegra), loratadine (brand Claritin) and cetirizine) (brand Zyrtec) are all considered newer antihistamines because they were designed to be safer than first generation antihistamines like Benadryl (diphenhydramine) as they do not cause drowsiness, or have very limited drowsiness. These newer antihistamines are non drowsy and can provide ample symptomatic relief for as long as 24 hours.
What is the Best Antihistamine for Hives?
There is not a single best antihistamine for hives, it depends on which antihistamine works for you. Commonly, people often try Benadryl for hives and while it is effective, it has a significant tradeoff - Benadryl is very sedating. So Benadryl may be effective for acute hives, Benadryl is not appropriate for chronic hives. Instead, a newer antihistamine with less sedating side effects like Curist Allergy Relief (levocetirizine), would be better antihistamine for treating hives.
What are the Common Side Effects of Allergy Antihistamines for Hives?
The most common side effect of antihistamines is drowsiness, but this is less of a problem with the non-sedating antihistamines used to treat hives. Other possible side effects may include headache, mood changes, nausea or dry mouth. If you are concerned about the drug interactions caused by hives medications with the other medicines you are currently taking, make sure to consult your doctor or pharmacist first.
What Helps Hives Besides Antihistamines?
Hives generally go away in a few hours, but some people may live with chronic hives or regular episodes. Here are a few proven home remedies that can help soothe your itchy skin:
- Use a cold compress: Apply an ice pack or washcloth soaked in cold water to your skin for 10 minutes to provide rapid relief from pain and itchiness. You may repeat it several times throughout the day until symptoms subside.
- Use anti-itch cream: Calamine lotion, menthol, capsaicin or hydrocortisone creams are the most effective in quickly relieving skin discomfort. Other topical anesthetics such as lidocaine cream can provide relief against long term itching or pain.
- Take a cool bath: Heat can make itching worse; while cool water can soothe the skin.
- Avoid triggers: If you are repeatedly experiencing episodes of hives, keep a symptom diary to help you identify foods, allergens (pollen or pet dander), chemicals, activities or medications that might be provoking allergic reactions. Avoid any triggers that you discover in your diary.
Lastly, to learn more about itchy skin and hives, read Curist team member Waverly’s story about her experiences diagnosing chronic hives and treating itchy skin.